The amazing world of peptides
The diversity of peptides
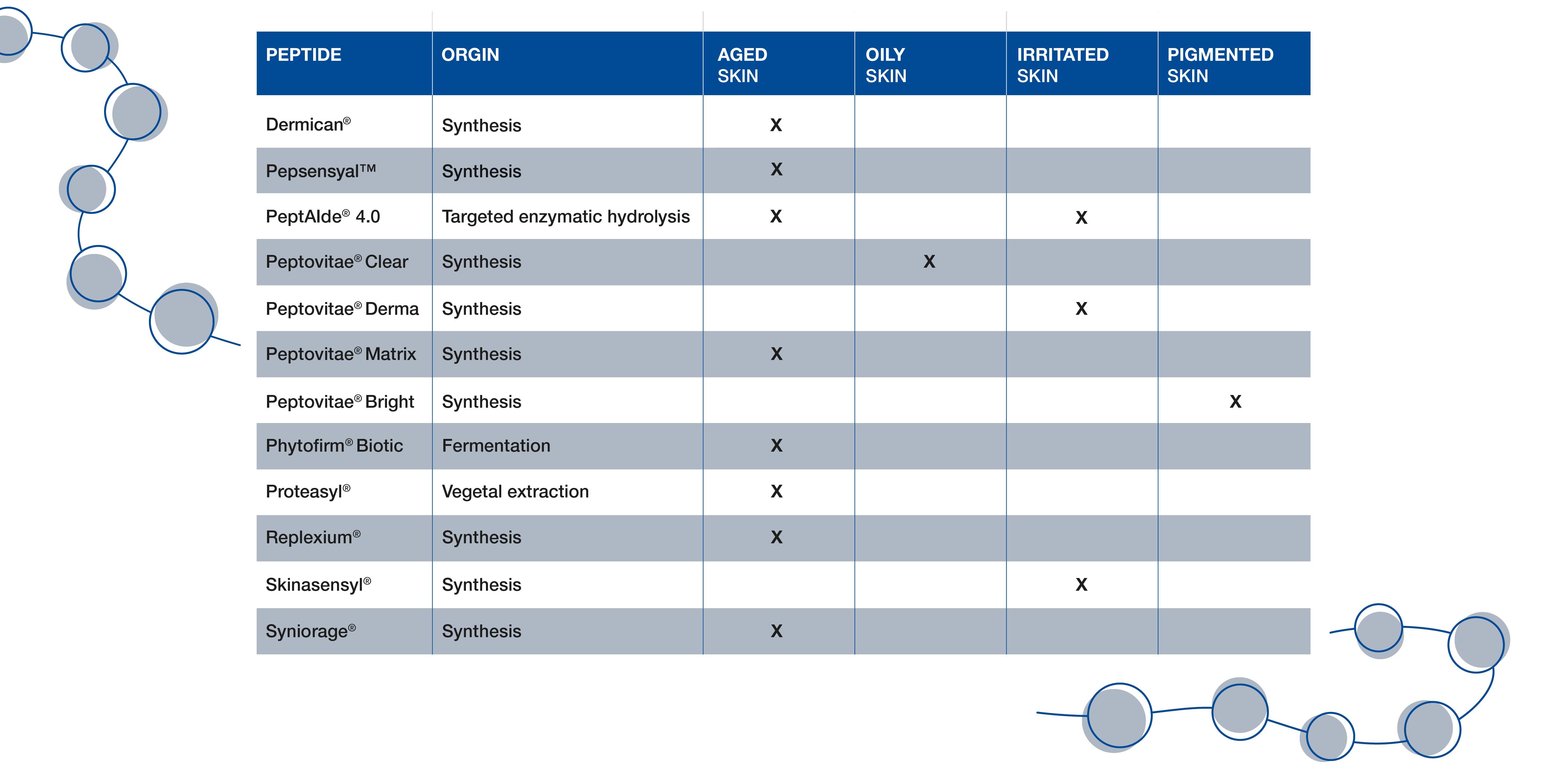
BASF’s active ingredient business unit was one of the first supplying the cosmetic industry with protein-based active ingredients with proven efficacy in the 1950s – at that time still from animal origin. BASF has since then followed an approach based on renewable vegetal resources, but complemented its portfolio with a range of synthetic peptides as well.
Today, BASF offers a complete active peptide portfolio, meeting any customer need. No matter what kind of cosmetic effect is targeted, or what manufacturing origin is preferred.
With the help of Artificial Intelligence, BASF identified four defined peptides that have specific action in the skin. We then excised these four peptides by a highly precise enzymatic method from a larger protein.
PeptAIde® 4.0 contains these four highly effective peptides as part of a hydrolysate of organic rice protein.
Innovation Focus: Peptides

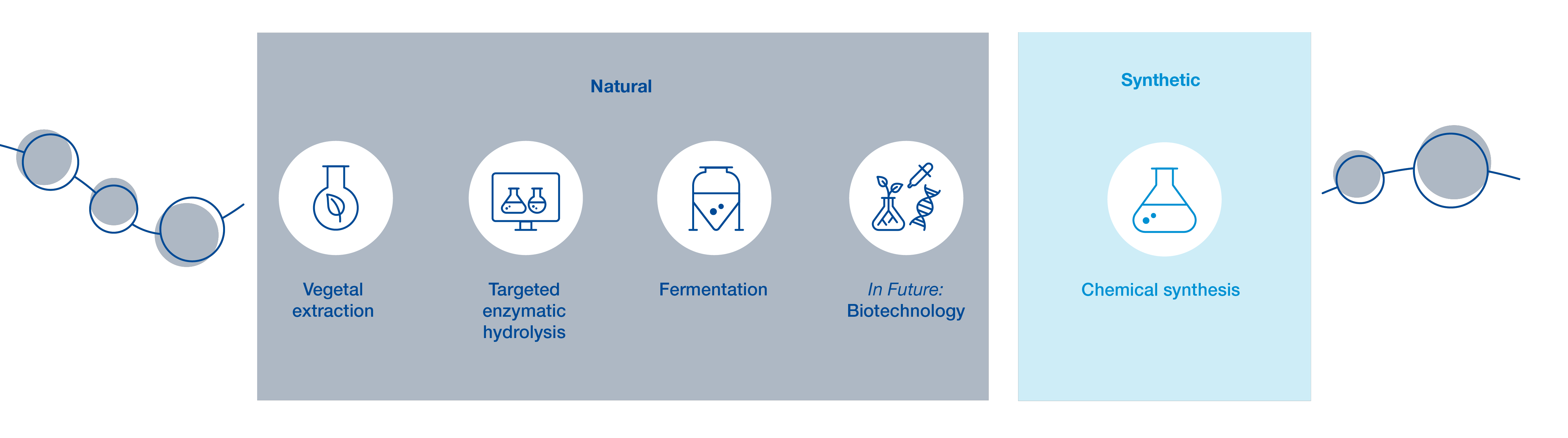
Vegetal extraction
Blend of peptides of varying chain length, extracted from natural raw materials
Proteasyl®:
Polypeptides from winter pea
Kerasylium™:
Plant-based alternative to keratin

Targeted enzymatic hydrolysis
Specific peptides derived from hydrolysis of a vegetal protein
PeptAIde® 4.0:
With 4 specific peptides, discovered by AI, and excised from organic rice protein
Fermentation
Peptides derived from fermentation of renewable raw materials
Phytofirm® Biotic:
Soybean extract biotransformed by Lactobacillus
In Future: Biotechnology
Specific peptides produced by microorganisms from renewable raw materials

Chemical synthesis
Short-chained, defined peptides
Peptovitae® range:
Biomimetic peptides in liposomes
Replexium®:
Synergistic blend of two acetylated tetrapeptides
Skinasensyl®, Syniorage®,
Dermican®, Pepsensyal™ :
Acetylated tetrapeptides
Highly efficiently targeting all skin conditions
More interested in peptide structures and properties?
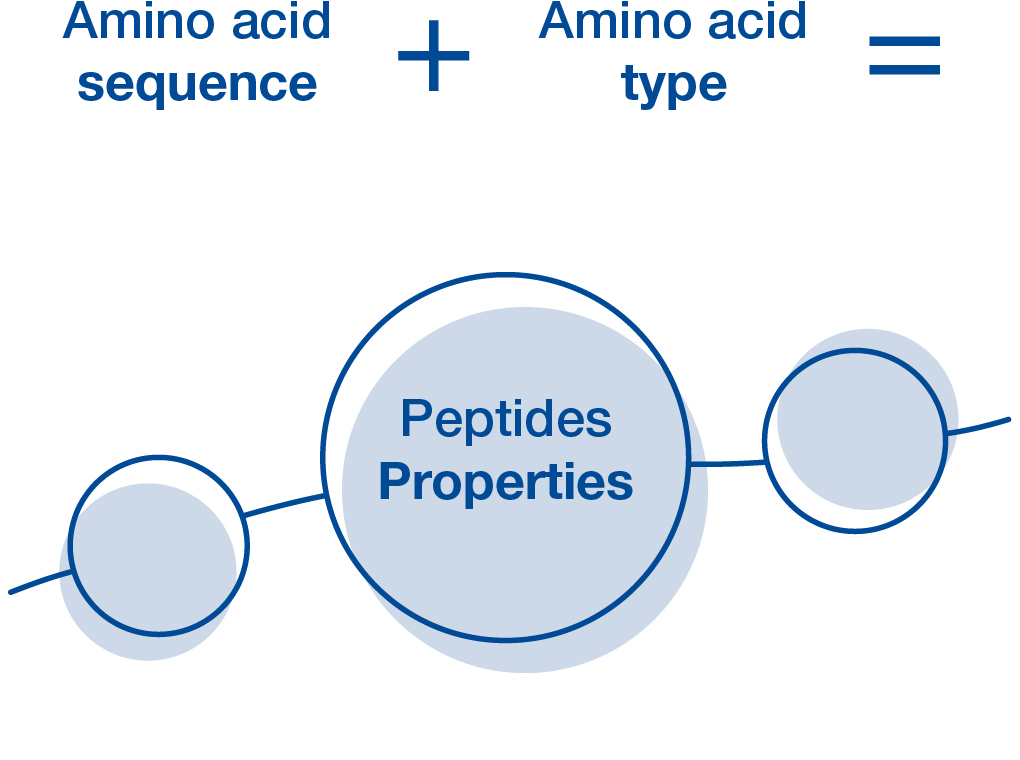
Peptides are natural molecules that occur in all organisms. They are characterized by the assembly of amino acids by a peptide bond. In the cosmetics context, the term “peptide” usually refers to small molecules that consist of less than 20 amino acids. The properties of peptides are determined by the type of amino acid and the sequence of amino acids.
Each amino acid sequence is linked to a certain physiological action. Peptides are like keys that unlock specific biological mechanisms in the skin, making peptides very effective active ingredients in cosmetics.
How to avoid the peptide INCI pitfall
Is there any chance to exploit peptides that are not listed under a peptide name in the PCPC or IECIC INCI lists? Yes: if the peptides are part of a natural extract or the hydrolysate of a natural protein.
Limited availability of peptides in cosmetics
The number of amino acids used to build the peptide structure determines the number of theoretically possible different sequences. If all 20 essential amino acids of the human body are considered, up to 104.857.600.000.000.000.000.000.000 different sequences are theoretically possible.
But for the INCI declaration of cosmetics, only approximately 72 INCI names with the term “peptide” are available in the list of the Inventory of Existing Cosmetic Ingredients in China (IECIC).
This restricted number of available INCI names are out of all proportion to the tremendous variety of possible peptides that might be effective in a cosmetic sense.
The popularity of peptides among both brands and consumers is due to the manifold roles that peptides play in the skin
As a major part of physiology of life is based on peptides, many biochemical effects in the skin depend on peptide biochemistry. Peptides assure cellular communication, defend skin via antimicrobial effects, inhibit enzymes degrading structural elements, or build supporting structures themselves, to name but a few. The proven benefits of peptides allow their use in a growing number of applications and formats, and consumers perceive these molecules as high-performing ingredients.
For those customers demanding pure, defined peptides obtained from synthesis, we offer our Peptovitae® range. These are synthetically derived, biomimetic peptides consisting of 10 to 13 amino acids with a low molecular weight between 1300 to 1600 Da. To increase bioavailability, they are encapsulated in liposomes. Already established are our tetrapeptides Syniorage®, Dermican®, Skinasensyl® and Replexium®.
Related Formulations Peptide
Replexium®
PeptAIde® 4.0
Skinasensyl®
Dermican®
Syniorage®
Syniorage
Phytofirm® Biotic
Phytofirm Biotic
PeptAIde® 4.0
In a cutting-edge process, enzymes that excise certain peptide sequences can be used to prepare the hydrolysate. This is how BASF enriched the four anti-inflammatory peptides in the hydrolysate of organic rice protein. The INCI of the rice protein hydrolysate can be used.
ExploreProteasyl®
Peptides can be part of an extract. The more specific the way the extract is produced, the higher the peptide content can be, and the more precise the characterization of the peptides can be. If the peptides in an extract are known, there is no need for further isolation, and the INCI of the extract can be used.
Explore